Introduction
In today’s digital era, the ability to capture, analyse and recreate the real-world objects in three dimensions has transformed the industries like construction, architecture, manufacturing and entertainment. At the mid of this change are two powerful technologies: 3D Point Clouds and 3D Meshes.
Both formats are essential for creating accurate digital twins thereby enabling the engineers, designers and project managers to make the smarter decisions. However, while point clouds excel in precision and measurement, meshes shine out in visualization and usability.
Understanding when to use each of these is critical for the successful project outcomes—whether you’re scanning a heritage site for preservation, designing a new product prototype or else creating the assets for entertainment.
This article breaks down their evolution, characteristics, practical applications and differences to help you decide which one suits your needs.
The Evolution of 3D Point Clouds and Meshes
- 3D Point Clouds emerged in the late 20th century with the development of LiDAR and high-resolution laser scanners. These technologies allowed the AEC professionals to capture millions of precise data points of the real-world environments.
- 3D Meshes, on the other hand, evolved primarily in the fields of computer graphics and CAD modeling where the smooth surfaces and realistic textures were needed. They later on became indispensable in industries like gaming, product design as well as in 3D printing.
Over the time both formats have grown complementary—point clouds captures the reality with highest accuracy whereas meshes transforms that data into user-friendly visual models.
What is a 3D Point Cloud?
A 3D Point Cloud is a dataset made up of millions of points in the 3D space each defined by X, Y and Z coordinates. This raw data is typically captured using the LiDAR, photogrammetry or laser scanning.
Key Characteristics of Point Clouds
- Highly Accurate: Point clouds can capture details with millimeter precision hence making them ideal for the surveys, inspections and also for the engineering analysis.
- Unstructured Data: They consist of the individual points and not the connected surfaces, which means that the specialized software is required for interpretation and processing.
- Data-Rich: Every point represents an exact position thereby allowing the engineers to work with reliable, real-world measurements.
Practical Uses
- Construction & Surveying: Provides detailed as-built documentation of sites hence reducing the errors during the planning and renovations.
- BIM Modeling: Acts as the foundation for creating the intelligent Building Information Models used in the architecture and engineering. Many companies rely on Point Cloud to BIM Services for this process.
- Heritage Preservation: Helps digitally archive the historical monuments with high precision for restoration projects. Many firms now offer Scan to Mesh Services to streamline these workflows.
What is a 3D Mesh?
A 3D mesh is a structured model composed of vertices, edges, and faces—typically triangles or quadrilaterals—that together create a seamless surface. Unlike point clouds, meshes provides smooth geometry that can be easily textured and rendered.
Key Characteristics of Meshes
- Surface-Based Structure: Meshes connect vertices to form polygons thereby creating a continuous, visually appealing surface.
- Visualization Friendly: They are easier to render, animate and integrate into the simulations compared to the raw point cloud data.
- Scalable & Flexible: Meshes can be optimized—denser meshes for highly-detailed models whereas lighter meshes for faster processings.
Practical Uses
- Product Design & Prototyping: Designers use meshes to create and refine the 3D models before any physical manufacturing.
- Gaming & Animation: Meshes forms the backbone of the 3D assets thereby allowing for the realistic character and environment creations.
- 3D Printing & Reverse Engineering: Meshes can be directly exported for additive manufacturing or used to reconstruct the mechanical parts.
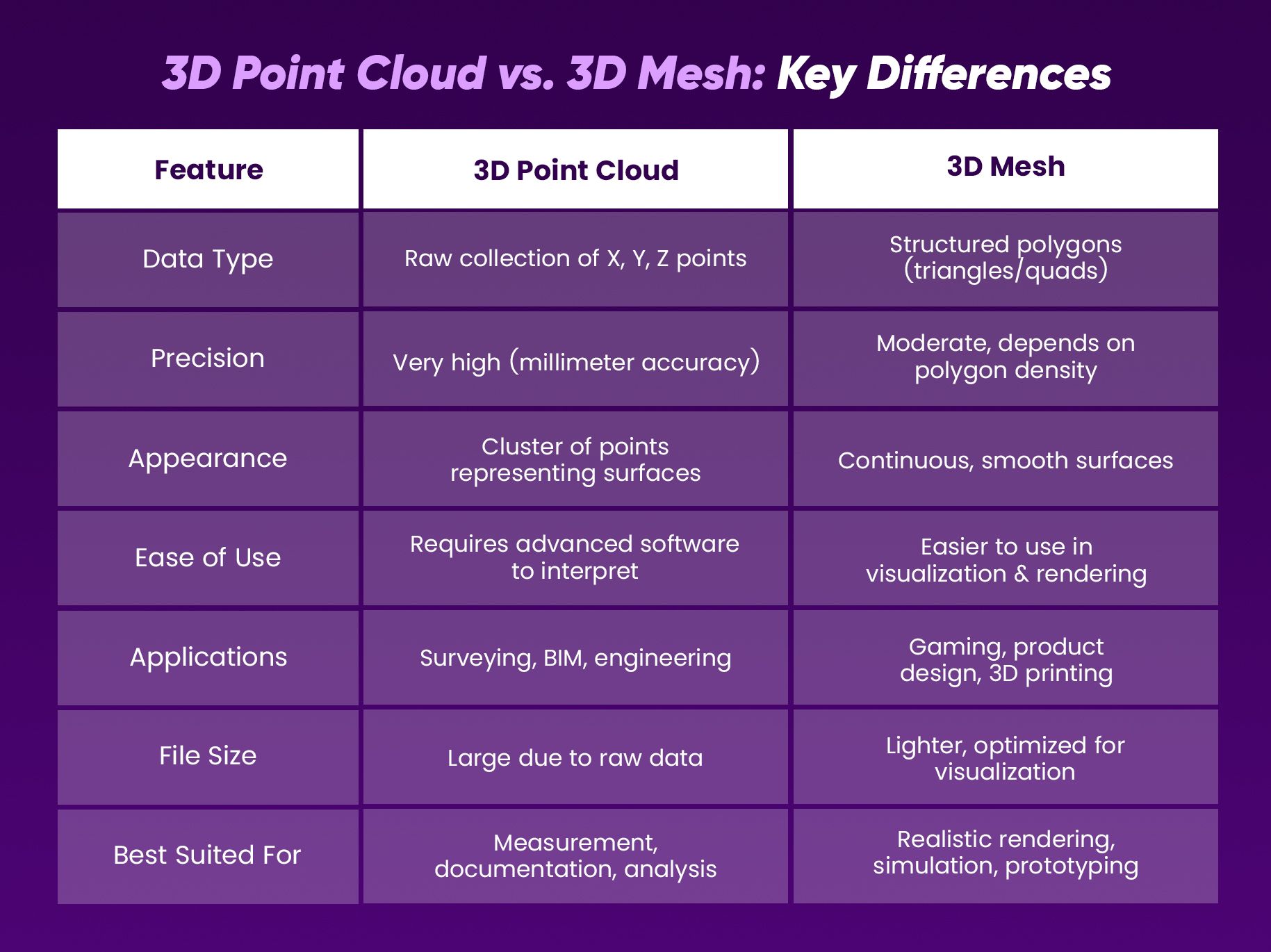
3D Point Cloud vs. 3D Mesh: Key Differences
When to Use Point Cloud vs. Mesh
- Use a Point Cloud when accuracy is non-negotiable—for example, scanning a construction site for renovation or conducting the structural analysis of an industrial plant.
- Use a Mesh when realism and usability matters—for example, creating a 3D model for a video game, designing a prototype for 3D printing or even for producing the marketing visualizations.
Conclusion
Both 3D Point Clouds and 3D Meshes are indispensable tools in the digital modeling ecosystem. Point clouds capture the world as it is—with unrivaled accuracy—while meshes makes that data usable in the design, visualization and manufacturing.
In practice, many projects rely on both: a point cloud for precise measurements and a mesh for visualization or simulation. By understanding their unique strengths, industries can seamlessly bridge the gap between the real-world accuracy and digital creativity.
FAQs on 3D Point Clouds and Meshes
- Can a 3D point cloud be converted into a mesh?
Yes, point clouds are often processed into meshes for easier visualization, rendering or even for the 3D printing. This process is common in workflows where both accuracy and usability are required. - Which is more accurate: a point cloud or a mesh?
Point clouds are generally more accurate since they capture the raw data points with millimeter precision. Meshes trade off some accuracy for smooth yet continuous surfaces as well as easier handling. - Are point clouds harder to work with than meshes?
Yes, point clouds require specialized software and more processing power. Meshes are simpler to interpret and are widely supported in design, visualization and printing applications. - Do industries use both point clouds and meshes together?
Absolutely. A point cloud may be captured for accuracy and then converted into a mesh for visualization or 3D printing. Many modern projects integrate both formats for maximum efficiency.